What is true regarding the thermal ecg paper – Thermal ECG paper is a specialized recording medium used in electrocardiography (ECG) to capture and display electrical signals from the heart. Understanding its properties, storage requirements, and troubleshooting techniques is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable ECG recordings.
This comprehensive guide explores the basics of thermal ECG paper, its physical and chemical characteristics, proper storage and handling practices, common troubleshooting issues, and alternative recording methods.
1. Thermal ECG Paper Basics

Thermal ECG paper is a specialized type of recording paper used in electrocardiography (ECG) machines. It is coated with a heat-sensitive layer that reacts to electrical signals from the heart, creating a visible trace of the electrical activity.
Thermal ECG paper is composed of several layers:
- A base layer made of paper or plastic
- A heat-sensitive layer containing a mixture of dyes and chemicals
- A protective top layer to prevent damage to the heat-sensitive layer
There are different types of thermal ECG paper available, each with its own specific properties:
- Standard thermal ECG paper:The most common type of thermal ECG paper, suitable for general ECG recordings.
- High-sensitivity thermal ECG paper:Designed for recording low-amplitude signals, such as those from pediatric patients.
- Grid thermal ECG paper:Features a grid pattern to facilitate measurement of intervals and amplitudes.
- Multi-channel thermal ECG paper:Used in multi-channel ECG machines, allowing for simultaneous recording of multiple leads.
2. Thermal ECG Paper Properties
The physical and chemical properties of thermal ECG paper play a crucial role in the quality of ECG recordings:
- Sensitivity:The ability of the paper to react to electrical signals and produce a visible trace.
- Resolution:The sharpness and clarity of the recorded trace, determined by the size of the heat-sensitive particles.
- Speed:The rate at which the paper moves through the ECG machine, affecting the time resolution of the recording.
- Stability:The ability of the recorded trace to resist fading or discoloration over time.
These properties are carefully controlled during the manufacturing process to ensure optimal performance and accurate ECG recordings.
3. Thermal ECG Paper Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling of thermal ECG paper are essential to maintain its quality and prevent damage:
- Storage:Store the paper in a cool, dry place, protected from light and moisture.
- Handling:Avoid touching the heat-sensitive layer, as fingerprints or dirt can interfere with recordings.
- Use:Use the paper within its recommended shelf life to ensure optimal performance.
Improper storage or handling can lead to reduced sensitivity, faded recordings, or inaccurate measurements.
4. Thermal ECG Paper Troubleshooting: What Is True Regarding The Thermal Ecg Paper
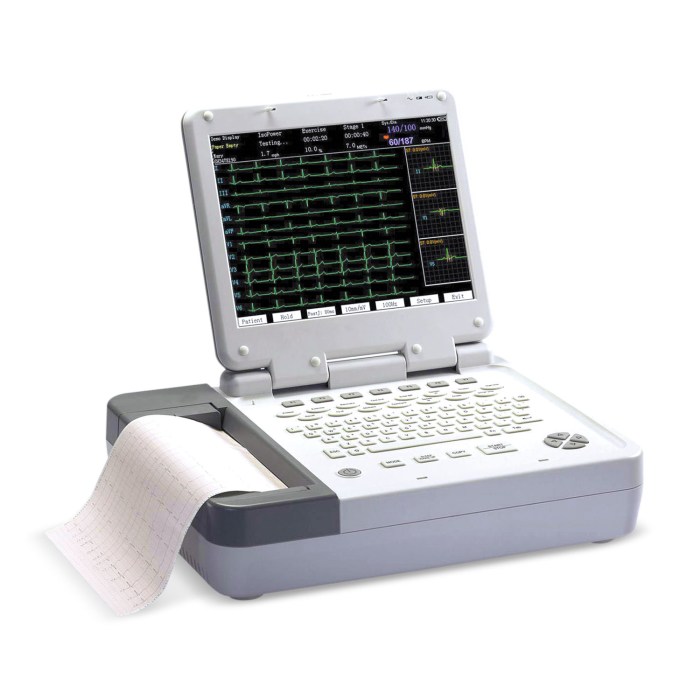
Common problems encountered with thermal ECG paper include:
- Faded recordings:Caused by improper storage or exposure to light.
- Reduced sensitivity:May indicate a damaged heat-sensitive layer or an issue with the ECG machine.
- Artifacts:Interference from external sources, such as electromagnetic fields.
Troubleshooting tips:
- Check the storage conditions and replace the paper if necessary.
- Inspect the heat-sensitive layer for damage and clean the ECG machine if needed.
- Identify and eliminate potential sources of interference.
5. Thermal ECG Paper Alternatives
Alternative recording methods for ECGs include:
- Digital ECG recording:Stores ECG data digitally, eliminating the need for thermal paper.
- Inkjet ECG recording:Uses inkjet technology to create a permanent record on plain paper.
- Film ECG recording:A traditional method that uses photographic film to capture ECG signals.
Each alternative has its own advantages and disadvantages compared to thermal ECG paper:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal ECG paper | Low cost, portable, easy to use | Fades over time, sensitive to environmental factors |
| Digital ECG recording | Permanent record, high-quality, versatile | Requires specialized equipment, more expensive |
| Inkjet ECG recording | Permanent record, cost-effective, compact | Lower resolution than thermal paper, slower printing speed |
| Film ECG recording | High-quality, permanent record | Requires chemical processing, expensive, bulky |
Quick FAQs
What are the key properties of thermal ECG paper?
Thermal ECG paper is characterized by its heat-sensitive coating, which reacts to electrical signals to produce visible traces. Its physical properties include thickness, weight, and opacity, while its chemical properties include sensitivity, stability, and archival quality.
How should thermal ECG paper be stored and handled?
Proper storage involves maintaining a cool, dry, and dark environment. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and light. Handle the paper carefully to prevent damage to the coating.
What are some common troubleshooting issues with thermal ECG paper?
Common issues include smudging, fading, or poor signal quality. These can be caused by improper storage, handling, or equipment malfunction. Troubleshooting involves checking paper quality, connections, and printer settings.
What are some alternative recording methods to thermal ECG paper?
Alternative methods include digital recording, ink-jet printing, and telemetry. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, such as cost, portability, and data quality.