Which constitutional principle is best illustrated by the chart? This question delves into the fundamental principles that shape the structure and functioning of a constitutional democracy. By examining the distribution of powers, the relationship between different levels of government, and the mechanisms for checks and balances, we can identify the constitutional principle that is most prominently reflected in the chart.
The chart provides a visual representation of the constitutional principles that govern the organization and operation of government. It illustrates the separation of powers among the branches of government, the division of power between the federal government and state governments, and the various checks and balances that prevent any one branch or level of government from becoming too powerful.
Separation of Powers
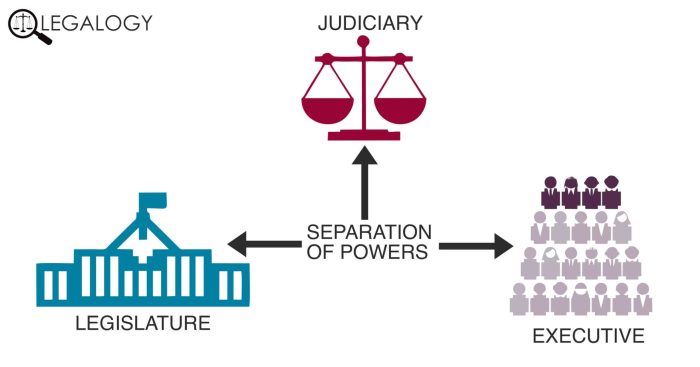
The chart illustrates the distribution of powers among different branches of government, namely the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Each branch has its own set of powers and responsibilities, and is designed to check and balance the other branches.
For example, the legislative branch has the power to make laws, while the executive branch has the power to enforce laws and the judicial branch has the power to interpret laws. This separation of powers prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful and ensures that the government remains accountable to the people.
Checks and Balances
In addition to the separation of powers, the chart also illustrates the checks and balances that exist between the branches of government. For example, the legislative branch can override a veto by the executive branch with a two-thirds vote, and the judicial branch can declare laws passed by the legislative branch to be unconstitutional.
These checks and balances help to ensure that no one branch of government can become too powerful and that the government remains accountable to the people.
Federalism: Which Constitutional Principle Is Best Illustrated By The Chart
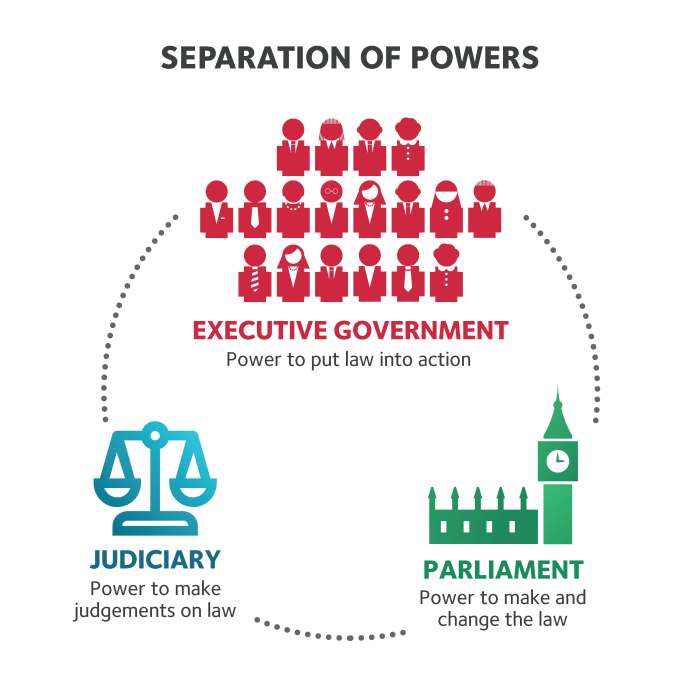
The chart demonstrates the division of power between the federal government and state governments. The federal government has certain powers that are delegated to it by the Constitution, such as the power to regulate interstate commerce and declare war. State governments have all powers that are not delegated to the federal government, such as the power to regulate intrastate commerce and education.
Reserved Powers and Delegated Powers
The reserved powers are those powers that are not delegated to the federal government and are therefore reserved to the states. The delegated powers are those powers that are specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Federalism
Federalism has a number of advantages, including the following:
- It allows for a more responsive government because state governments are closer to the people they represent.
- It protects individual rights because state governments can act as a check on the power of the federal government.
- It promotes economic growth because it allows states to compete with each other for businesses and jobs.
However, federalism also has some disadvantages, including the following:
- It can lead to conflict between the federal government and state governments.
- It can make it difficult to solve national problems because state governments may have different priorities.
- It can be expensive to maintain two levels of government.
Checks and Balances
The chart identifies the different mechanisms used to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. These mechanisms include the separation of powers, checks and balances, and the rule of law.
How Checks and Balances Work in Practice
In practice, checks and balances work in a number of ways. For example, the legislative branch can override a veto by the executive branch with a two-thirds vote, and the judicial branch can declare laws passed by the legislative branch to be unconstitutional.
Additionally, the president can veto laws passed by Congress, and Congress can impeach and remove the president from office.
Examples of Checks and Balances
There have been a number of examples of checks and balances being used to resolve conflicts between different branches of government. For example, in 1793, President George Washington vetoed a bill passed by Congress that would have established a national bank.
Congress was unable to override the veto, and the bill was not passed.
In another example, in 1803, the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Marbury v. Madison that a law passed by Congress was unconstitutional. This was the first time that the Supreme Court had declared a law unconstitutional, and it established the principle of judicial review.
Rule of Law
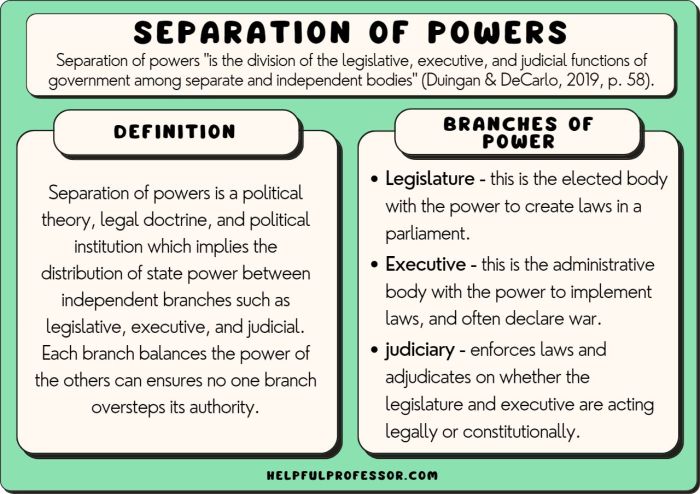
The chart reflects the principle that everyone, including government officials, is subject to the law. This principle is essential to a free and democratic society because it ensures that no one is above the law.
How the Rule of Law Protects Individual Rights and Freedoms
The rule of law protects individual rights and freedoms in a number of ways. For example, the rule of law prohibits the government from depriving people of their life, liberty, or property without due process of law. Additionally, the rule of law guarantees the right to a fair trial and the right to an attorney.
Examples of the Rule of Law
There have been a number of examples of the rule of law being upheld in the United States. For example, in 1954, the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Brown v. Board of Education that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional.
This decision helped to end segregation in schools and was a major victory for the civil rights movement.
In another example, in 1974, the Supreme Court ruled in the case of United States v. Nixon that President Nixon could not assert executive privilege to prevent the release of tapes that were subpoenaed by Congress. This decision helped to establish the principle that no one is above the law, not even the president.
Popular Sovereignty
The chart demonstrates that the government derives its power from the consent of the governed. This principle is known as popular sovereignty and is essential to a free and democratic society.
How Citizens Can Participate in Government
There are a number of ways that citizens can participate in government. These include voting, running for office, serving on juries, and contacting elected officials.
Examples of Popular Sovereignty
There have been a number of examples of popular sovereignty in the United States. For example, in 1776, the Declaration of Independence declared that all men are created equal and that governments derive their power from the consent of the governed.
This principle was later enshrined in the Constitution.
In another example, in 1861, the American Civil War was fought over the issue of slavery. The war ended with the abolition of slavery and the establishment of the principle that all men are created equal.
Limited Government

The chart reflects the principle that the government’s power is limited. This principle is essential to a free and democratic society because it prevents the government from becoming too powerful.
How the Government’s Power Can Be Limited, Which constitutional principle is best illustrated by the chart
There are a number of ways that the government’s power can be limited. These include the separation of powers, checks and balances, the rule of law, and popular sovereignty.
Examples of Limited Government
There have been a number of examples of limited government in the United States. For example, the Constitution limits the power of the federal government by dividing it into three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Additionally, the Constitution guarantees certain individual rights and freedoms, such as the right to free speech and the right to bear arms.
In another example, in 1937, the Supreme Court ruled in the case of United States v. Butler that the Agricultural Adjustment Act was unconstitutional because it exceeded the powers delegated to the federal government by the Constitution. This decision helped to establish the principle that the government’s power is limited.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the most important constitutional principle?
The most important constitutional principle is the rule of law, which means that everyone, including government officials, is subject to the law.
What is the purpose of the separation of powers?
The purpose of the separation of powers is to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
What are the advantages of federalism?
The advantages of federalism include the protection of individual rights, the promotion of economic growth, and the prevention of tyranny.