Do i have cirrhosis quiz – Embark on our interactive quiz, “Do I Have Cirrhosis?”, and uncover the truth about your liver health. This journey will shed light on the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for this condition, empowering you with knowledge and insights.
Cirrhosis is a serious liver disease that can lead to life-threatening complications. Understanding your risk factors and recognizing the early signs is crucial for timely intervention and improved outcomes. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of cirrhosis and provide you with the tools to make informed decisions about your health.
Definition and Symptoms
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue. It is primarily caused by excessive alcohol consumption, chronic viral hepatitis (such as hepatitis B and C), and autoimmune disorders. Other factors that can contribute to cirrhosis include non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hemochromatosis, and biliary diseases.
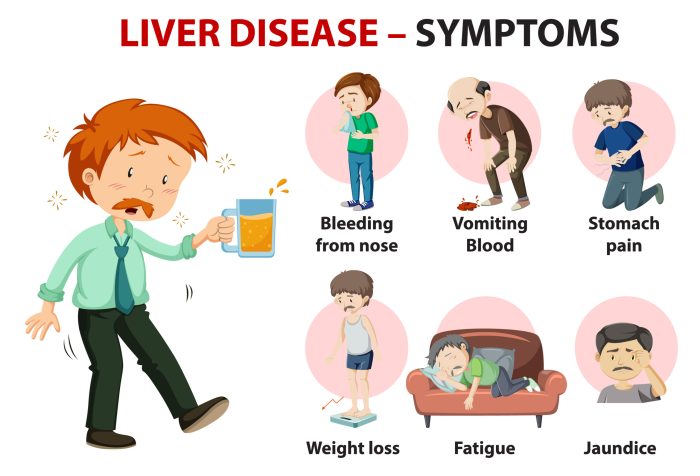
The symptoms of cirrhosis can vary depending on the severity of the disease. In the early stages, there may be no noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, swelling in the legs and ankles (edema), and yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
Physical Manifestations, Do i have cirrhosis quiz
- Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity
- Splenomegaly: Enlargement of the spleen
- Spider angiomas: Small, red, spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- Palmar erythema: Redness of the palms
- Gynecomastia: Enlargement of breast tissue in men
- Clubbing of fingers: Enlargement and rounding of the fingertips
Risk Factors and Causes: Do I Have Cirrhosis Quiz
Cirrhosis, a late-stage liver disease, is often the culmination of various risk factors and underlying causes that gradually damage the liver over time.
Let’s delve into the major factors that can contribute to cirrhosis and the underlying conditions that trigger liver damage.
Major Risk Factors
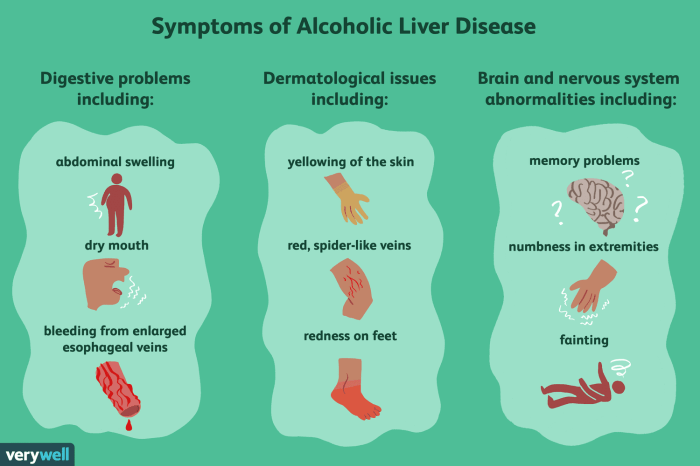
- Chronic Alcohol Abuse:Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is a leading cause of cirrhosis. Alcohol can directly damage liver cells, leading to inflammation and scarring.
- Viral Infections:Hepatitis B and C viruses are the most common viral causes of cirrhosis. These viruses infect and damage liver cells, causing inflammation and scarring.
- Autoimmune Disorders:Certain autoimmune disorders, such as autoimmune hepatitis, can attack the liver, leading to inflammation and scarring.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):NAFLD, caused by fat accumulation in the liver, can progress to cirrhosis if left untreated.
- Genetic Conditions:Some genetic conditions, such as hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease, can cause cirrhosis by disrupting liver function.
Underlying Causes
- Viral Hepatitis:Hepatitis B and C viruses cause chronic inflammation and scarring of the liver, eventually leading to cirrhosis.
- Alcoholic Liver Disease:Alcohol abuse damages liver cells, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis:This autoimmune disorder causes the body’s immune system to attack the liver, leading to inflammation and scarring.
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC):PBC is an autoimmune disorder that damages the bile ducts, leading to liver damage and cirrhosis.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):PSC is an autoimmune disorder that damages the bile ducts, leading to liver damage and cirrhosis.
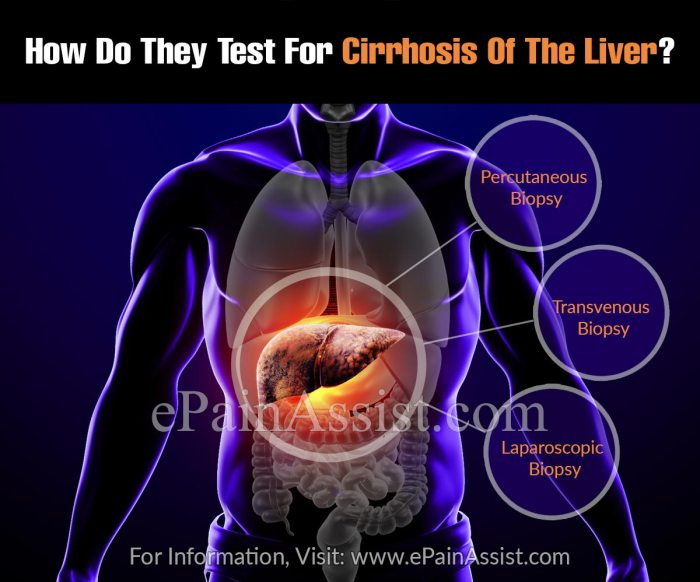
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing cirrhosis involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging techniques. These tests help assess liver function, identify the underlying cause, and determine the severity of the condition.
Do you suspect you might have cirrhosis? Taking an online quiz can provide some insight, but for a more comprehensive assessment, consider exploring EM 385 1 1 test answers . This resource offers a range of diagnostic questions that can help you determine the severity of your condition and guide you towards appropriate medical care.
Returning to the topic of cirrhosis, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice if you experience persistent symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, or yellowing of the skin.
Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
LFTs measure the levels of various enzymes, proteins, and bilirubin in the blood. Elevated levels of these substances can indicate liver damage or dysfunction. Some common LFTs include:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Total bilirubin
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques provide visual representations of the liver and surrounding structures. They can help detect changes in liver size, shape, and texture, as well as identify any abnormalities or scarring.
- Ultrasound:Uses sound waves to create images of the liver, showing its size, shape, and any abnormalities.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):Utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the liver, providing information about its structure, blood flow, and any scarring.
- Biopsy:A small sample of liver tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to evaluate the extent of scarring and inflammation.
Treatment Options and Management
Managing cirrhosis involves addressing the underlying cause, preventing further liver damage, and managing complications. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of cirrhosis and the underlying cause.
Antiviral Medications
For cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis, antiviral medications are prescribed to suppress the virus and slow down liver damage. These medications can improve liver function and reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing cirrhosis. These include:
- Diet:A healthy diet low in sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods can help reduce fluid retention and improve liver function.
- Exercise:Regular exercise can help maintain muscle mass and improve overall health.
- Alcohol abstinence:Alcohol consumption can further damage the liver and worsen cirrhosis.
- Smoking cessation:Smoking can constrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the liver.
Liver Transplantation
In severe cases of cirrhosis where other treatments are not effective, liver transplantation may be an option. Liver transplantation involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy one from a donor. This is a major surgery with potential risks and complications.
Complications and Prognosis
Cirrhosis can lead to various complications that significantly impact overall health and quality of life. These complications may arise due to the scarring and impaired liver function caused by cirrhosis.
Impact on Overall Health
Cirrhosis affects multiple organ systems, including the kidneys, brain, and lungs. It can cause fluid retention (ascites), swelling in the legs (edema), and impaired blood clotting. The accumulation of toxins in the bloodstream can lead to hepatic encephalopathy, a condition that affects brain function and can result in confusion, drowsiness, and even coma.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with cirrhosis depends on several factors, including the underlying cause of liver damage, the stage of cirrhosis, and the presence of complications. Early detection and treatment of cirrhosis can improve the prognosis and slow the progression of the disease.
However, cirrhosis is a serious condition, and the prognosis can be poor if it is not managed effectively.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of cirrhosis?
Symptoms may include fatigue, yellowing of the skin and eyes, swelling in the legs and abdomen, easy bruising or bleeding, and loss of appetite.
What are the major risk factors for cirrhosis?
Risk factors include excessive alcohol consumption, chronic hepatitis B or C infection, autoimmune disorders, and certain genetic conditions.
How is cirrhosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, blood tests (liver function tests), and imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI.